Brain Aneurysm: What Is It And How To Prevent It
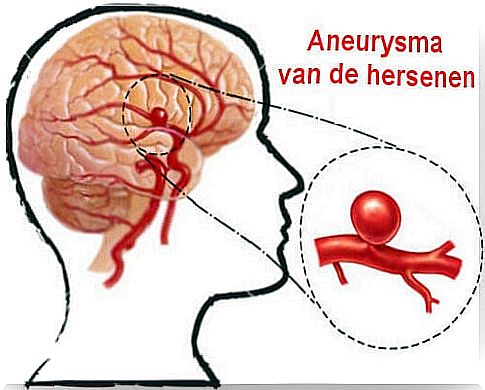
A brain aneurysm. You may have heard people talk about it or you or a family member may have experienced one. It’s because small blood vessels in the brain fill up with blood and put dangerous pressure on them.
This is something to keep in mind because a percentage of it has to do with your lifestyle habits. Want to know more about this? Keep reading.
1. What is a brain aneurysm?
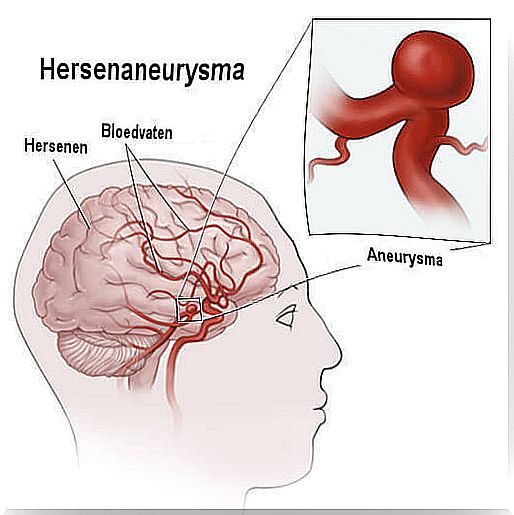
The word itself might startle you. But you don’t have to. Usually these problems are solved well with a timely intervention. The most important thing to know about this is how to identify the symptoms and try to live a healthy life.
To go into more detail, a brain aneurysm occurs when a vein in the brain fills with blood and at the same time creates pressure, especially on that part of the head.
It normally tends to happen in the lower part of the brain and so you have to keep that in mind. If not caught in time, it can lead to serious problems.
The risk is that two things may happen: This pressure causes irreparable damage or this blood vessel begins to bleed.
2. But what causes a brain aneurysm?

Is there a clear cause that can be determined to prevent them ? The answer is “yes and no”.
In many cases it can be a congenital pathology or in other words you can be born with these small blood vessels already swollen in your brain.
Another possibility is that the brain aneurysm is caused by other diseases, such as a kidney problem, circulation problems, or problems in your veins and arteries.
Infections, high blood pressure, head injuries, certain cancers … All of that can also lead to these small and dangerous accumulations of blood in the brain, interrupting circulation.
3. Who is most at risk for a brain aneurysm?

That is the adult population, usually between 30 and 60 years old. We should point out that according to the statistics, women are at greater risk of suffering from a brain aneurysm.
The blood vessels are considered a serious risk when they are 15 mm in size in the brain, so there is a potential risk that they will begin to bleed and thereby put greater pressure on the brain.
This would be the moment when the true risks arise. If they burst and bleed in the brain, a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) will occur, which will also lead to new aneurysms.
4. What are the symptoms?

Unfortunately, many brain aneurysms show no symptoms until the blood vessels are large or burst. If they are small, or in other words less than 10mm in size, you won’t notice anything happening either. But if they’re bigger than that and still growing, you’ll start to notice the effects.
What are the consequences? How do you know if you have a brain aneurysm that is about to burst? You will notice pain behind and above your eyes in particular, weakness or paralysis on one side of your face and also your pupils are somewhat dilated.
It is also worth knowing the symptoms associated with a brain aneurysm that has already started bleeding:
- sudden and severe headache,
- wake up with double vision
- nausea
- pain in the neck
- pass out
Other signs include:
- drooping eyelids
- be more sensitive to light
- not being able to concentrate normally
- convulsions
- having the worst headache ever
If the symptoms are very obvious, you should contact a doctor right away to get this checked out.
5. How is a brain aneurysm diagnosed?
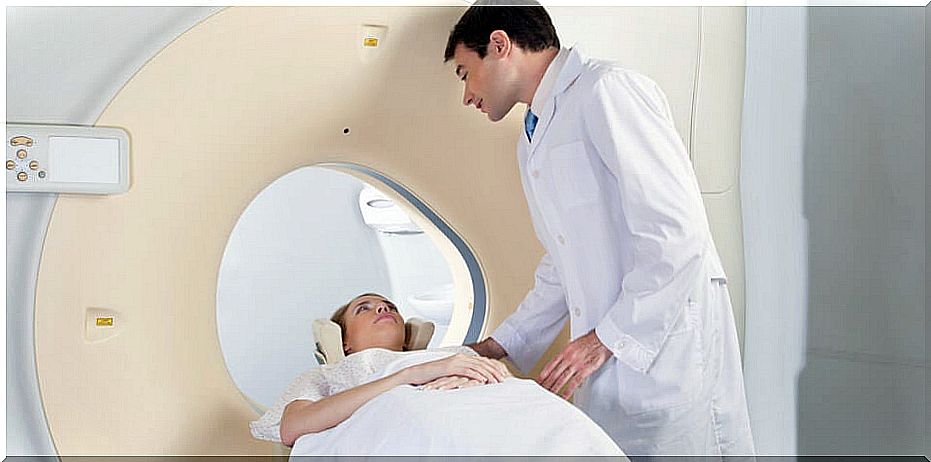
To check whether you have a brain aneurysm, you should always have a CAT scan or an MRI scan. Sometimes a brain aneurysm is accidentally revealed when patients are being monitored for other diseases.
6. How is a brain aneurysm treated?
First, we should mention that every patient is unique and depending on personal factors and the size of the aneurysm, the doctors will choose a way. They will likely use both techniques.
The first way is the microvascular clipping, which attempts to cut off the blood supply to the aneurysm.
The doctor gains access to the vessel that supplies blood to the aneurysm and then puts a small, metal clip on the neck of the aneurysm, similar to a buckle, to prevent the aneurysm from coming back.
The other technique is not done in the brain, but consists of endovascular embolization. What the doctor does is put a catheter through the artery in the groin, which leads a platinum coiled wire to the aneurysm. It will block the blood there and the problem will be solved.
Today the techniques are very advanced and you don’t have to be afraid. Brain aneurysms tend to resolve well. We just need to be aware of the symptoms.