Compulsive Nail Biting And Oral Health

Compulsive nail biting, or onychophagia, doesn’t just cause aesthetic problems to your hands. It also has consequences for your oral health. The habit of putting the fingers in the mouth is usually an unconscious action. Often it is an indicator of an emotional conflict or is an imitated behavior.
This problem can affect people of all ages, but is more common in childhood and adolescence. However, in some people it continues into adulthood. While this habit may seem harmless, it can damage the mouth. Read on to find out how.
What is onychophagia?
Onychophagia is the name given to the habit of biting nails. It is a compulsive and unconscious behavior where a person puts their fingers in the mouth and nibbles on the area at the end of the fingers.
Although the term refers specifically to the nails, it is also used for nibbling on the surrounding soft tissues, i.e. the skin around the nails. Another way to refer to the disorder is by the name dermatophagia.
However, this word refers to a slightly more serious disorder, in which the nails are sometimes even pulled out and swallowed. It has to do with psychiatric conditions such as obsessive-compulsive disorder, depression, or body dysmorphic disorder.
The origin of compulsive nail biting is usually related to stress. When faced with repeated situations of anxiety that they cannot adequately resolve, the gesture and act serve as stress relievers.
There is also a hypothesis associated with the patient’s persistence in the oral stages of psychological development. This would explain the tendency to put things in the mouth, including their fingernails.
General health problems caused by compulsive nail biting

Compulsive nail biting has specific oral health implications that we will analyze later. But first, let’s look at what happens in other body systems when this compulsive act is involved. This is outside of the associated psychiatric conditions that may be present, which have their own signs and symptoms.
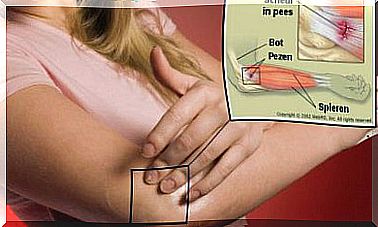
At the digestive level, ingesting the bits of nail that come off with biting can alter the way the stomach processes food. For example, it is possible that the production of stomach acid increases and that dyspepsia occurs, or, in other words, non-specific discomfort in the upper abdomen.
As we descend further into the digestive tract, we also see the consequences in the small intestine. There, the pieces of nail can facilitate the entry of parasites, which can settle in the gut and cause symptoms depending on the parasite species.
Onychomycosis is another consequence. This is a fungal infection of the nails. The nails are damaged and are in constant contact with the mouth. As a result, the surrounding humidity increases and molds get a favorable environment to settle.
Nail mycosis is difficult to treat and requires long-term treatment with the use of special nail polish and drugs. Therefore, it is a condition that must be detected early.
Onychomycosis is the fungal infection of the nails. One speaks of paronychia (English link) when the soft tissues around the hard part of the fingers are infected. Just the repeated biting helps the microorganisms to penetrate the subcutaneous tissue.
The Effects of Compulsive Nail Biting on Oral Health
Although the digestive system, the nails themselves and the skin of the fingers are the most affected areas, compulsive nail biting also leads to undeniable consequences for oral health. Both the teeth and the rest of the structures of the oral cavity are sensitive to this.
Let’s not forget that hands are always in contact with foreign substances and pathogens. We use these extremities on a daily basis to connect with the world around us.
With our hands we come into contact with viruses, bacteria, parasites and dirt, which then end up in our mouths when we bite our nails. But this is not all. There is also mechanical stress on the surface of the teeth that can wear down the enamel and even cause gum disease.
Now let’s look at some oral health consequences of onychophagia, which we can prevent by reducing the habit.
1. Compulsive nail biting causes premature tooth wear
One of the consequences of onychophagia for oral health is the wear and tear of the tooth enamel. This happens due to the friction of the nails against the teeth and the rubbing of the teeth against each other. The nail breaks when biting. Then the teeth of the upper arch transfer their mechanical stress to the lower arch. This leads to repeated microtrauma.
The microtrauma consists of microfractures and in extreme cases of actual fractures in the surface of the teeth. Although there is no breakage as such, there is continuous and premature wear.
The upper central incisors are most commonly affected, due to their position and exposure to this habit. This is more evident in people who suffer from onychophagia due to stress and anxiety, as they usually also suffer from bruxism (clamping and grinding of the teeth).
2. Compulsive nail biting increases the risk of cavities
Cavities are a common condition of the mouth. Their presence is explained by poor hygiene and oral care resulting in bacterial colonization responsible for the fermentation of dietary carbohydrates.
This process produces acids that demineralize the tooth. So, what would be the consequence of onychophagia in this case? It turns out that the bacteria present on the fingers and nails increase the colonization of the oral cavity.
The more bacteria there are, the greater the fermentation and the more acids can demineralize the hard tissues of the tooth. As a result, the risk of cavities increases (Spanish link).
3. Halitosis
Halitosis is the official name for bad breath. The causes are diverse, but the most common are related to poor oral hygiene and bacterial colonization. Therefore, a bad smell in the mouth is one of the consequences of compulsive nail biting.
As we said before, this compulsive habit can be part of major psychiatric disorders, affecting general hygiene. For example, a depressed person will tend not to take care of their appearance and may not brush their teeth as often as they should.
Bacteria carried from the teeth to the mouth by onychophagia contribute to the development of halitosis. The hands come into contact with various external micro-organisms that end up in the oral cavity.
4. Compulsive nail biting can lead to oral infections
The mouth has a flora of healthy microorganisms. For example, there are bacteria that normally occur in the oral cavity and do not cause disease. However, frequent contact with the hands and unknown pathogens disrupts this balance.
We have already mentioned that cavities are caused by the ingress of bacteria, but other infections are possible. Herpes labialis, for example, can be contracted through direct contact with the virus.
The halitosis we talked about isn’t always an isolated sign. Sometimes it is the manifestation of an ongoing infection caused by bacterial overgrowth.
- It is worth mentioning here periodontitis as a serious consequence of onychophagia in terms of oral health.
- At the same time, some mouth ulcers or canker sores are related to the colonization by microorganisms . These are very painful sores that disappear after about a week.
5. Temporomandibular Disorders

The temporomandibular joint can suffer from the effects of onychophagia because the constant mechanical stress of chewing can alter its function. This leads to pain when chewing food and abnormal jaw movements.
If we add bruxism as a result of generalized stress , the risk of joint dysfunction increases. Some patients start having ear pain as a manifestation of the disorder, due to the proximity of the structures together.
There is evidence that bad habits cause temporomandibular disorders, so it is not surprising to associate compulsive nail biting with this effect on oral health. The problem is that it is not only difficult to eliminate the repetitive action of nail biting. It is also difficult to correct a dysfunction of this joint.
How do you avoid the effects of compulsive nail biting on oral health?
If we want to avoid the oral health consequences of compulsive nail biting, we need to take some measures to reduce the bad habit. These can range from psychological treatment to home remedies and natural remedies to get rid of the desire to bite.
When there is a startling change that affects the quality of life or causes physical disorders such as those we have already mentioned, it is a good idea to arrange psychological treatment with a professional. Depending on his specialization, the psychologist will use different techniques for the approach.
A state of anxiety, depression, or stress that may underlie the onychophagia will also be treated. However, each case is individual and the methods will be individualized depending on the situation.
At the same time, the patient himself can apply home techniques to reduce the desire to bite the nails. Think, for example, of meditation, yoga, deep breathing or other methods that are aimed at managing stress.
In addition, there are nail polishes for sale that give the nail an unpleasant taste. This is done to discourage the habit of biting it. There are also artificial nails with the same function.
As far as dentistry is concerned, the first recommendation is to do a consultation. The dentist or hygienist can determine if there is already damage and address it, as well as recommend ways to hinder the habit. If deemed necessary, he will refer the nail biter to a psychologist.
Compulsive nail biting has health consequences
Onychophagia appears to be a minor problem when its consequences are not fully understood. However, its ultimate effect on the teeth, digestive system and skin should not be underestimated.
If you or a loved one regularly bites their nails, we recommend that you start by asking for advice. That could be a dentist, a psychologist or a doctor. There may be a background of stress or anxiety that can be resolved with proper treatment.